Loading... ## 前言 为了专注业务实现,我们采用 **枚举** + **CompletableFuture** + **自定义线程池**,封装了一套并行处理业务的工具类,便于在大数据和批处理场景中高效利用线程池。枚举天然具备单例特性,确保线程池的唯一性;同时,不同业务场景可以创建专属单例线程池,以实现任务隔离,防止资源相互干扰。 ## 实现 ```java package com.pilot.meterage.web.utils; import cn.hutool.core.date.LocalDateTimeUtil; import cn.hutool.core.util.ObjectUtil; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import javax.annotation.Nonnull; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.function.Supplier; import java.util.stream.Collectors; /** * 使用 CompletableFuture 实现简单的线程池 * * @author yangp */ public enum CompletableFutureSimpleThreadPool { /** * 单例对象 */ INSTANCE; /** * 自定义线程池,用于执行任务 */ private final ThreadPoolExecutor singleThreadPool; /** * 初始化线程池,并设置线程池参数 */ CompletableFutureSimpleThreadPool() { // 初始化线程池,核心线程数为15,最大线程数为20,线程空闲超时时间为30秒 singleThreadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 15, 20, 30L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000), r -> new Thread(r, "CompletableFutureUtils - " + r.hashCode()) ); } private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CompletableFutureSimpleThreadPool.class); // JVM 关闭时自动关闭线程池 static { Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> { log.info("[线程池] JVM 关闭前自动关闭线程池..."); INSTANCE.shutdown(); })); } /** * 执行多个任务(无返回值) * * @param tasks 任务数组 */ public static void executeTasks(@Nonnull Runnable... tasks) { if (ObjectUtil.isEmpty(tasks)) { logCheckTaskIsEmpty(); return; } long start = logTaskStart(); // 使用线程池并行执行多个任务 CompletableFuture<?>[] futures = Arrays.stream(tasks) .map(task -> CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { try { task.run(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("任务执行失败", e); } }, INSTANCE.singleThreadPool)) .toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new); // 打印线程池状态 logThreadPoolStatus(); // 等待所有任务执行完成 CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).join(); logTaskEnd(start); } /** * 执行多个任务(有返回值,使用 CompletableFuture 作为任务) * * @param tasks 任务数组 * @return 任务执行结果的列表 */ @SafeVarargs public static <T> List<T> executeCompletableFutures(@Nonnull CompletableFuture<T>... tasks) { List<T> results; if (ObjectUtil.isEmpty(tasks)) { logCheckTaskIsEmpty(); return Collections.emptyList(); } long start = logTaskStart(); // 使用 allOf 等待所有任务完成 CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(tasks); allOf.join(); // 收集任务结果 results = Arrays.stream(tasks) .map(CompletableFuture::join) .collect(Collectors.toList()); logTaskEnd(start); return results; } /** * 执行多个任务(有返回值,使用 Supplier 作为任务) * * @param tasks 任务数组 * @return 任务执行结果的列表 */ @SafeVarargs public static <T> List<T> executeSuppliers(@Nonnull Supplier<T>... tasks) { List<T> results; if (ObjectUtil.isEmpty(tasks)) { logCheckTaskIsEmpty(); return Collections.emptyList(); } long start = logTaskStart(); // 执行多个任务并收集结果 List<CompletableFuture<T>> futures = Arrays.stream(tasks) .map(task -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { return task.get(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("任务执行失败", e); return null; // 或者可以选择抛出 RuntimeException } }, INSTANCE.singleThreadPool)) .collect(Collectors.toList()); // 打印线程池状态 logThreadPoolStatus(); // 获取所有任务的执行结果 results = futures.stream() .map(CompletableFuture::join) .collect(Collectors.toList()); logTaskEnd(start); return results; } /** * 记录线程池当前的状态,包括当前线程池大小和任务数量 */ private static void logThreadPoolStatus() { log.info("[线程池状态] 池大小:{},活跃线程数:{},排队任务数:{},总任务数:{},完成任务数:{}", INSTANCE.singleThreadPool.getPoolSize(), INSTANCE.singleThreadPool.getActiveCount(), INSTANCE.singleThreadPool.getQueue().size(), INSTANCE.singleThreadPool.getTaskCount(), INSTANCE.singleThreadPool.getCompletedTaskCount()); } /** * 记录任务为空的情况 */ private static void logCheckTaskIsEmpty() { log.error("[线程池][执行任务] 任务为空"); } /** * 记录任务开始执行 */ private static long logTaskStart() { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("[线程池][执行任务] 开始时间:{},开始执行任务", LocalDateTimeUtil.now()); return startTime; } /** * 记录任务执行结束 */ private static void logTaskEnd(long start) { log.info("[线程池][执行任务] 结束时间:{},执行任务结束,耗时:{}ms", LocalDateTimeUtil.now(), System.currentTimeMillis() - start); } /** * 关闭线程池(单例线程池应该在 JVM 关闭时才被终止) */ public void shutdown() { log.info("[线程池] 正在关闭线程池..."); singleThreadPool.shutdown(); try { if (!singleThreadPool.awaitTermination(SHUTDOWN_TIMEOUT_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { log.warn("[线程池] 线程池未在规定时间内关闭,强制关闭"); singleThreadPool.shutdownNow(); } log.info("[线程池] 线程池已关闭"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("[线程池] 线程池关闭时被中断", e); singleThreadPool.shutdownNow(); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } /** * 线程池关闭超时时间(单位:秒) */ public static final long SHUTDOWN_TIMEOUT_SECONDS = 60; } ``` ## 测试 ```java package com.pilot.meterage; import com.pilot.meterage.web.MainApplication; import com.pilot.meterage.web.utils.CompletableFutureSimpleThreadPool; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; /** * @Author: yangp * @Date: 2024/11/12 14:41 */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = MainApplication.class) public class CompletableFutureTest { @Test public void test02() { Runnable run1 = () -> { // 模拟耗时 try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("run1"); }; Runnable run2 = () -> { // 模拟耗时 try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("run2"); }; Runnable run3 = () -> { // 模拟耗时 try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("run3"); }; Runnable run4 = () -> { // 模拟耗时 try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("run4"); }; CompletableFutureSimpleThreadPool.executeTasks(run1, run2, run3, run4); System.out.println("test02 执行完毕"); } @Test public void test03() { CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(CompletableFutureTest::getData1); CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(CompletableFutureTest::getData2); CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(CompletableFutureTest::getData3); List<String> res = CompletableFutureSimpleThreadPool.executeCompletableFutures(future1, future2, future3); System.out.println(res); System.out.println("test03 执行完毕"); } @Test public void test04() { List<String> res = CompletableFutureSimpleThreadPool.executeSuppliers(CompletableFutureTest::getData1, CompletableFutureTest::getData2, CompletableFutureTest::getData3); System.out.println(res); System.out.println("test04 执行完毕"); } public static String getData1() { // 模拟耗时 try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("data1执行完毕"); return "data1"; } public static String getData2() { // 模拟耗时 try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("data2执行完毕"); return "data2"; } public static String getData3() { // 模拟耗时 try { Thread.sleep(6000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("data3执行完毕"); return "data3"; } } ``` ## 真相 --- 测试案例1,并行执行通过 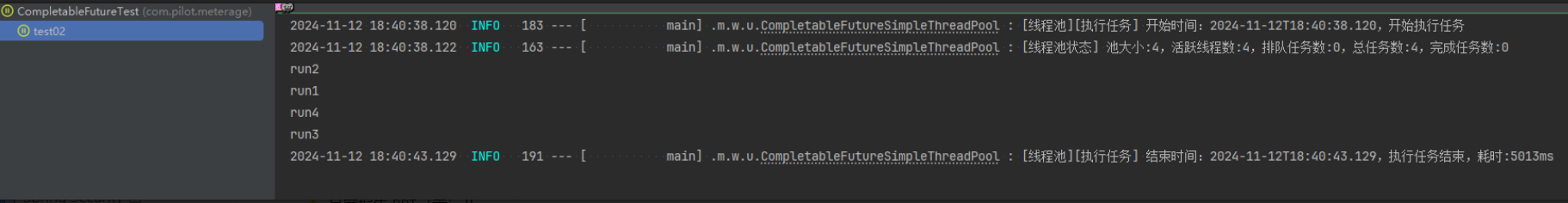 测试案例2,并行执行通过 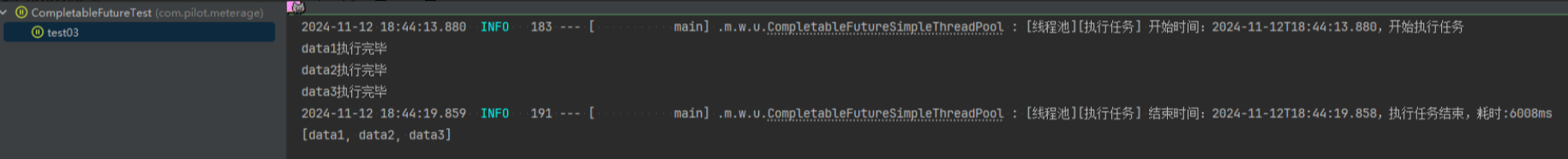 测试案例3,并行执行通过 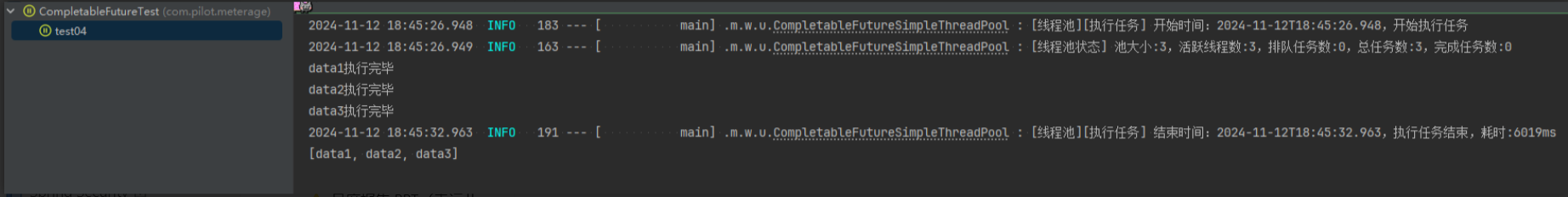 --- 最后修改:2024 年 11 月 12 日 © 允许规范转载 打赏 赞赏作者 支付宝微信 赞 如果文章有用,请随意打赏。